AWS HIPAA Compliance: A Comprehensive Guide & Checklist
Learn how to achieve and maintain HIPAA compliance on AWS with this comprehensive guide. Understand the shared responsibility model, essential architectural principles, and a practical checklist to protect PHI and avoid costly compliance violations. Discover how automation can reduce human error and streamline your security posture.

Mélanie Dallé
September 9, 2025 · 11 min read
#Key Points:
- Shared Responsibility is Key: AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud (the underlying infrastructure), while customers are responsible for security in the cloud (configuring services, managing access, and encrypting data). Understanding this division is essential to avoid compliance failures.
- Human Error is a Major Risk: The most significant risks to HIPAA compliance often stem from manual processes, such as configuration errors, inconsistent deployments, and a lack of training. These human factors can lead to compliance drift and costly violations.
- Automation Is the Solution: Using automation and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) can eliminate human error, ensure consistent security configurations, and maintain continuous compliance. This approach embeds security directly into the development workflow, providing a more reliable path to protecting patient data.
In the world of modern healthcare, patient data is everything. It's the key to ground-breaking new treatments and a vital part of everyday care, but it's also a prime target for hackers. As more and more healthcare organizations move their operations to the cloud, like on AWS, keeping that data safe is not just a good idea—it's a legal and ethical must. HIPAA is the rulebook we all have to follow, but getting it right on a huge platform like AWS can feel like navigating a maze.
This guide is here to help. We'll walk you through the most important things to know, give you a handy checklist, and show you how using smart automation can save you from big headaches and major security risks. Think of this as your practical roadmap to building secure, compliant applications without all the stress.
#What is HIPAA and Why Compliance Matters?
HIPAA compliance protects patient privacy while enabling healthcare innovation. The regulation applies to healthcare providers as well as their business associates who handle protected health information (PHI). They include any individually identifiable health information transmitted or stored during processing.
Organizations must protect PHI through three types of safeguards: administrative, physical, and technical. These safeguards work together to create comprehensive protection for sensitive healthcare data.
#AWS Shared Responsibility Model
AWS operates under a shared responsibility model where security and compliance responsibilities are divided between AWS and the customer. Understanding this division is crucial for maintaining HIPAA compliance.
#AWS Responsibilities (Security of the Cloud)
AWS manages the security of the underlying infrastructure, including physical facilities, hardware, software, networking, and managed services. AWS maintains HIPAA-eligible services and provides the foundation for building compliant applications through regular security audits and certifications.
#Customer Responsibilities (Security in the Cloud)
Customers are responsible for securely configuring their AWS services, which includes managing access controls, encrypting data, and implementing logging and monitoring. A critical component of this responsibility is ensuring logs retention and auditability. Customers must establish policies for how long logs—like those from AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch Logs—are stored, often to meet regulatory requirements that can span years.
To ensure these logs are useful for security audits and investigations, they must be auditable, meaning they are immutable and tamper-evident. This can be achieved by using services like Amazon S3 with WORM (write-once, read-many) policies, which prevent logs from being altered or deleted, thereby preserving their integrity and ensuring they can serve as a reliable source of truth for compliance and security reviews.
Many compliance failures result from misunderstanding these responsibilities. Customers must actively implement security controls rather than relying solely on AWS default configurations.
#Building a HIPAA-Compliant Architecture on AWS
#1. Architectural Principles
HIPAA-compliant architectures on AWS must incorporate several fundamental principles. Network isolation creates secure boundaries around PHI using Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and proper subnet design. Encryption protects data both in transit and at rest using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and service-specific encryption options.
Access control ensures only authorized personnel can access PHI through carefully configured IAM policies and role-based permissions. Audit logging captures all access and changes to PHI using CloudTrail and service-specific logs. Monitoring and alerting provide real-time visibility into security events and potential compliance violations.
#2. Essential AWS Services for HIPAA Compliance
a. Encryption Services
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) provides centralized key management for encrypting data across AWS services. Amazon EBS encryption protects data volumes, while S3 server-side encryption secures object storage with minimal performance impact.
b. Networking and Access Control
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) creates isolated network environments with configurable subnets and security controls. Security Groups act as virtual firewalls, controlling traffic at the instance level. Identity and Access Management (IAM) controls who can access AWS resources and what actions they can perform.
c. Monitoring and Logging
AWS CloudTrail records API calls and user activity across your AWS account, providing a complete audit trail. Amazon CloudWatch monitors resources and applications, generating alerts for security events. These services provide the visibility necessary for compliance reporting.
d. Storage and Database Services
Amazon S3 provides scalable object storage with built-in encryption and access logging. Amazon RDS offers managed database services with encryption, automated backups, and audit logging capabilities. Both services support HIPAA workloads when properly configured.
#AWS HIPAA Compliance Checklist
#1. Administrative Safeguards
- Designate a security officer responsible for HIPAA compliance and a privacy officer to oversee privacy-related policies and procedures. This is a crucial step for accountability.
- Develop and maintain written information security policies, including a comprehensive breach response plan. This plan should detail the steps for detecting, containing, and mitigating a breach, as well as the process for notifying affected parties and regulatory bodies.
- Execute a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with AWS, clearly outlining AWS's responsibilities under the shared responsibility model.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) for all systems interacting with PHI, ensuring that user access is limited to the minimum necessary information required for their job function.
- Establish training programs for all workforce members on HIPAA requirements, including how to handle PHI, recognize and report security incidents, and follow the breach notification protocols.
- Document access authorization processes and maintain logs of all approvals and changes to access rights. This includes a clear process for onboarding and offboarding employees.
#Organizational Safeguards
- Establish an Incident Response Plan that specifically addresses data breaches. This plan should define roles, responsibilities, and communication workflows for both the covered entity and its business associates (like AWS).
- Create and maintain clear procedures for breach notification. This includes defining the process for notifying affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and potentially the media within the required timeframes (typically no later than 60 days after discovery).
- Utilize AWS logs to gather information for breach notifications. The incident response plan should detail how to query and analyze logs from services like AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch to determine key details of a breach, such as what data was compromised, who was affected, and the scope of the incident. This is vital for fulfilling the notification requirements.
- Maintain and test the breach notification process through periodic drills and tabletop exercises. This ensures the organization is prepared to act swiftly and accurately in the event of a real security incident.
#Physical Safeguards
- Verify AWS data center security certifications, recognizing that physical access to AWS infrastructure is managed by AWS.
- Implement workstation use restrictions for accessing PHI. This includes policies on where workstations can be used, prohibiting the use of personal devices for accessing PHI, and mandating automatic logoff for inactive sessions.
- Build rigorous access control processes for your own facilities where PHI is handled or stored. This includes using badges, biometric readers, or other authentication methods to limit access to secure areas.
- Establish media controls for PHI storage and disposal. This involves policies for securely moving, storing, and disposing of any hardware or media (e.g., hard drives, USBs) that have contained PHI, ensuring data is irretrievably destroyed.
#Technical Safeguards
Access Control
- Configure IAM policies with least privilege principles, ensuring users only have permissions to the services and data necessary for their role.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts, especially for users with administrative privileges or those accessing sensitive data.
- Implement automatic logoff for inactive user sessions to prevent unauthorized access from unattended workstations.
- Use unique user identification for each system user to enable accountability and detailed activity tracking in logs.
Audit Controls
- Enable AWS CloudTrail in all regions to record all API calls and a wide range of other actions. This creates a comprehensive audit trail of activity.
- Configure CloudWatch for real-time monitoring of logs, setting up alerts for anomalous and suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or changes to critical resources.
- Implement log aggregation and analysis, using a service like Amazon S3 for secure, long-term storage of logs and a service like Amazon Athena or a third-party SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tool for efficient querying and analysis of that data.
- Configure alerts for anomalous and suspicious activities, such as unusual login times, access from new locations, or an unusually high number of API calls, to enable proactive threat detection.
Integrity Controls
- Enable versioning for S3 buckets containing PHI. This creates a record of every version of an object, protecting against accidental or malicious deletion or modification.
- Encrypt all data in transit using TLS 1.2 or higher, ensuring that PHI is protected as it moves between a customer's systems and AWS services.
- Configure VPN connections for remote access to prevent unauthorized access over public networks.
- Implement network segmentation for PHI systems, isolating them from other parts of the network to minimize the blast radius of a potential breach. This can be achieved using AWS security groups and network access control lists (ACLs).
#Why Human Factors Create Major HIPAA Risks
#1. Configuration Errors and Manual Processes
Manual infrastructure setup introduces significant compliance risks through human error. Misconfigured security groups can inadvertently expose databases to the internet, while incorrect IAM policies might grant excessive permissions. These configuration mistakes often go unnoticed until security audits reveal vulnerabilities.
Common errors include leaving default security group rules in place, failing to enable encryption on storage services, or misconfiguring network access controls. Each error creates potential HIPAA violations and exposes organizations to regulatory penalties.
#2. Lack of Training
Insufficient training on HIPAA requirements and AWS security best practices leads to poor decision-making. Developers might choose convenience over security, using overly permissive IAM policies or storing PHI in unencrypted formats.
Lack of training can also impact personal security around password management, phishing attack detection, or improper management of sensitive data.
#3. Inconsistent Processes
Decentralized, manual deployment processes create inconsistent environments that are difficult to audit and maintain. When different team members configure infrastructure manually, variations in security settings become inevitable, making it challenging to verify compliance across all systems.
#4. Compliance Drift
Initially compliant environments can gradually become non-compliant through ad hoc changes and configuration drift. Without automated enforcement mechanisms, teams may make incremental changes that individually seem harmless but collectively compromise security posture.
Regular audits may catch these issues, but often only after significant drift has already occurred. Urgent business requirements can pressure teams to bypass established security procedures, accelerating compliance degradation.
#The Role of DevOps Automation Services in AWS HIPAA Compliance
#1. Eliminating Human Error
Automated infrastructure deployment eliminates the configuration errors that manual processes introduce. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) ensures consistent, repeatable deployments that follow security best practices. Automated testing validates configurations before deployment, catching potential compliance issues early.
Automation also provides audit trails for all infrastructure changes, making it easier to track modifications and verify compliance over time. This visibility is essential for HIPAA audit requirements and incident response procedures.
#2. Compliance as Code
Treating compliance requirements as code allows teams to version control, test, and deploy security configurations alongside application code. This approach embeds security and compliance into the development workflow rather than treating it as a separate concern.
Automated monitoring systems can detect compliance violations in real-time and trigger remediation workflows. These systems provide continuous assurance that environments remain compliant as they evolve.
#How Qovery Simplifies AWS HIPAA Compliance
Qovery provides a DevOps automation tool that streamlines the deployment of HIPAA-compliant applications on AWS. The platform abstracts infrastructure complexity while maintaining the security controls necessary for healthcare applications.
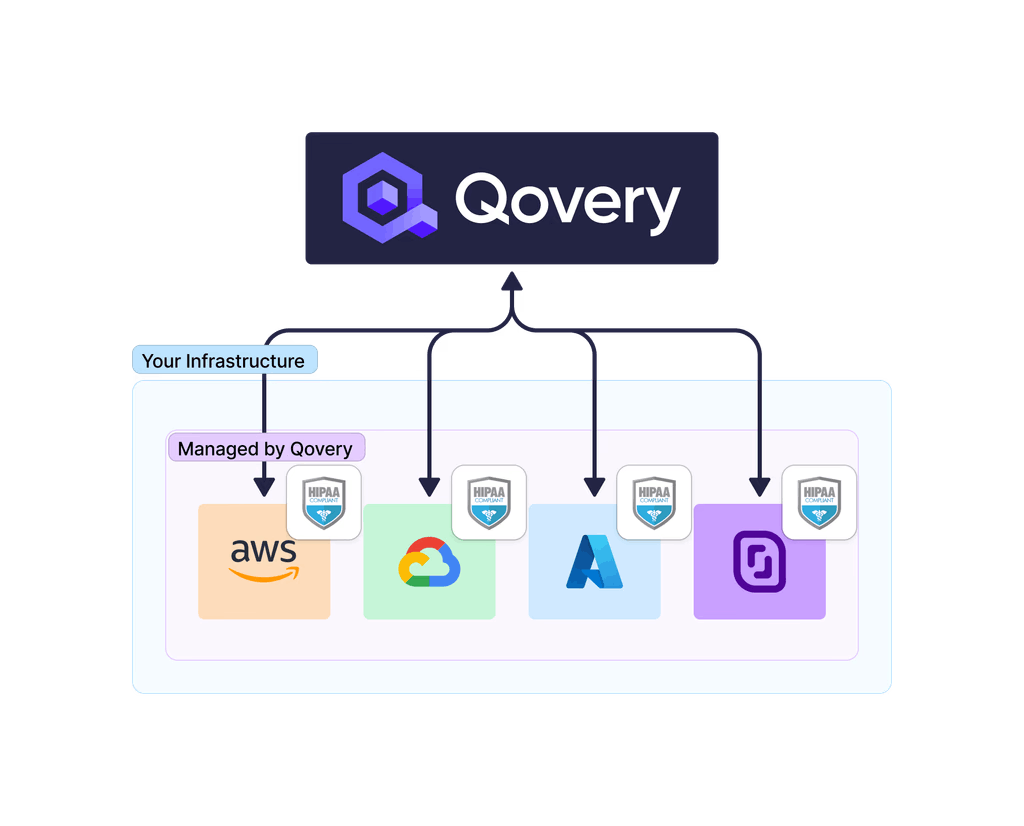
#1. Consistent, Compliant Deployments
Qovery ensures every application deployment follows pre-configured, HIPAA-compliant infrastructure templates. The platform automatically configures VPCs, security groups, encryption settings, and monitoring tools according to healthcare industry best practices. This consistency eliminates the configuration variations that manual deployments introduce.
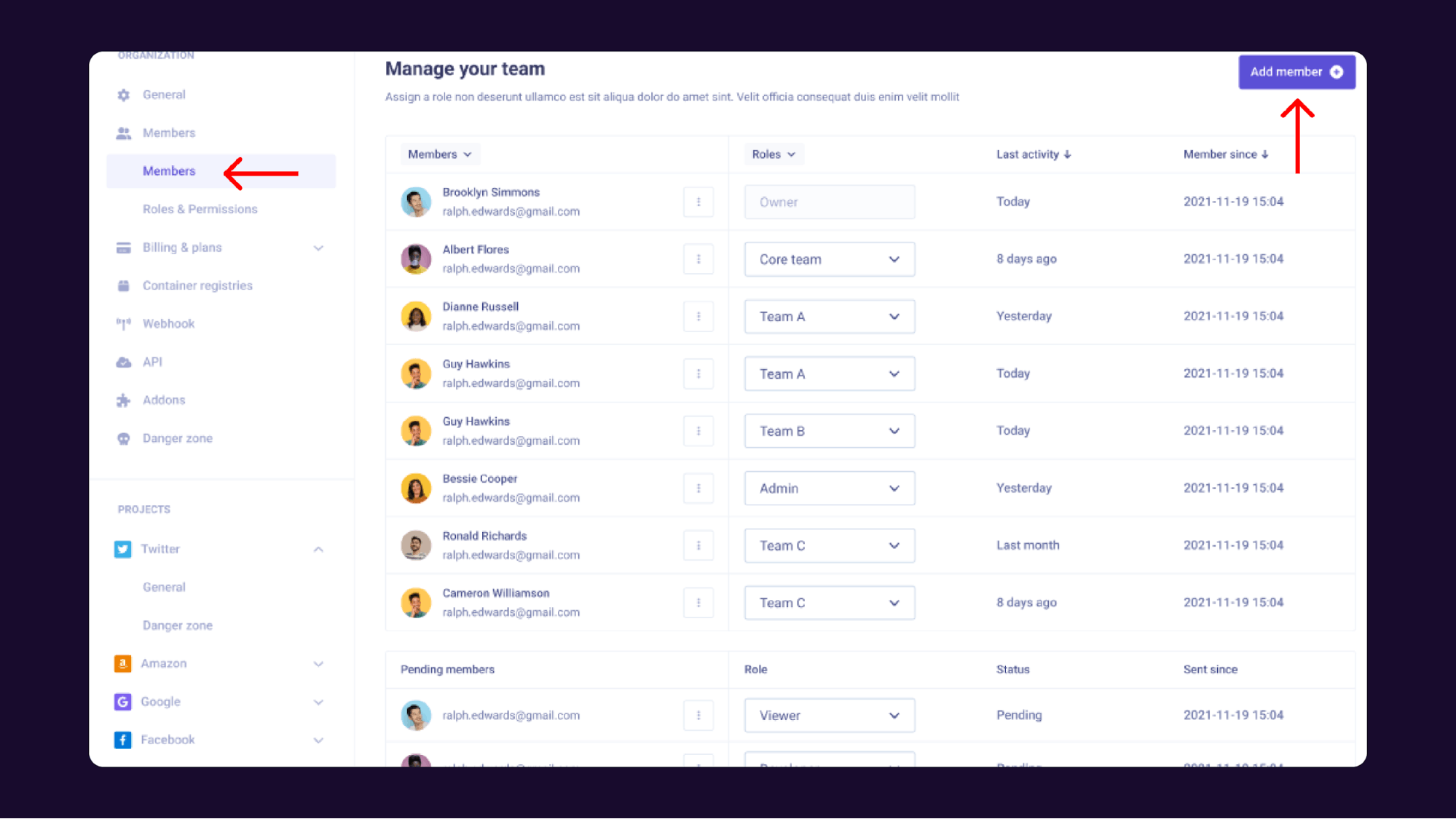
#2. Simplified Access Control
The platform simplifies IAM role and permission management by providing pre-configured access control templates for healthcare applications. Qovery automatically implements least privilege principles and role-based access controls.
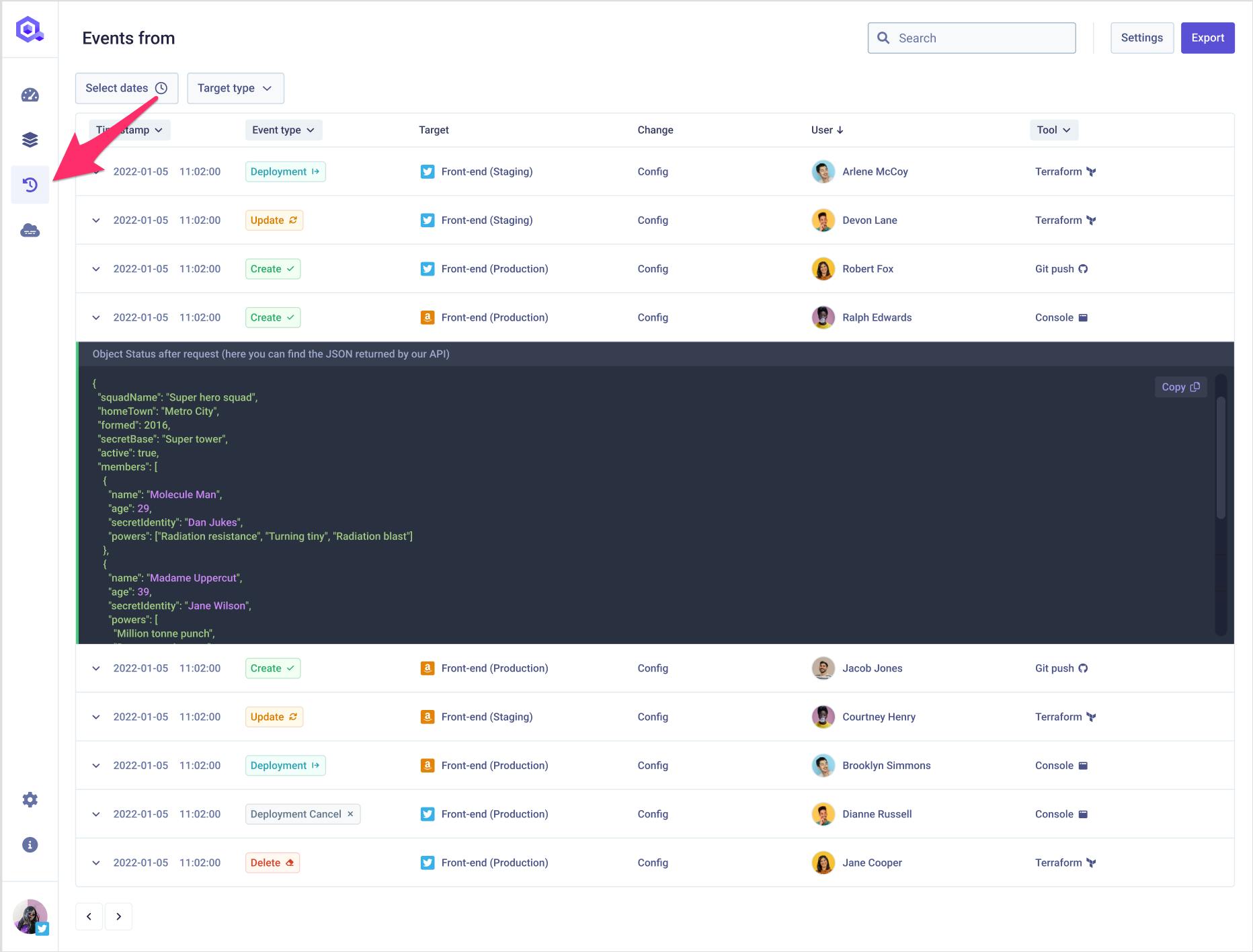
#3. Enhanced Auditability
Qovery provides centralized visibility into all application deployments and infrastructure changes. The platform maintains comprehensive logs of deployment activities, configuration changes, and access events, simplifying compliance audits and incident investigations.
#4. Automated Security Best Practices
The platform implements security best practices by default, including encryption at rest and in transit, network isolation, and secure configuration management. Qovery's HIPAA compliance platform capabilities include automated backup procedures, disaster recovery configuration, and continuous security monitoring.
By automating infrastructure management and security configuration, Qovery reduces the operational burden on engineering teams. Developers can focus on building healthcare applications rather than managing complex AWS security configurations.
#Simplify Your HIPAA Compliance Journey with Qovery
Achieving HIPAA compliance on AWS requires careful attention to architectural design, security configuration, and ongoing monitoring. While AWS provides the foundation, it's up to you to implement the right controls under the shared responsibility model.
Manual approaches are a significant liability. They create risks through configuration errors, inconsistent processes, and compliance drift. Automation, however, provides a more reliable path. By eliminating human error and ensuring consistent, secure deployments, automation platforms like Qovery make HIPAA compliance more accessible than ever before.
Healthcare organizations that invest in automated compliance processes are better positioned for sustainable growth and innovation without compromising patient data.
#Ready to try Qovery?
Boost your DevOps efficiency, accelerate compliance, enhance security, and drive innovation with Qovery.
- 🚀 Sign up for Qovery’s trial.
- 📅 Book a demo to discuss how Qovery simplifies HIPAA compliance while accelerating your team's deployments.
Your Favorite DevOps Automation Platform
Qovery is a DevOps Automation Platform Helping 200+ Organizations To Ship Faster and Eliminate DevOps Hiring Needs,
Try it out now!

Your Favorite DevOps Automation Platform
Qovery is a DevOps Automation Platform Helping 200+ Organizations To Ship Faster and Eliminate DevOps Hiring Needs,
Try it out now!


.jpg?ixlib=gatsbyFP&auto=compress%2Cformat&fit=max)


